How a Battery Works
Chemistry 3 of 3
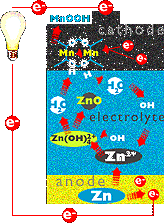 OXIDATION and reduction could not occur in a battery without a way to carry
electrons back to the anode after they enter the cathode. Here's
where the electrolyte comes in.
OXIDATION and reduction could not occur in a battery without a way to carry
electrons back to the anode after they enter the cathode. Here's
where the electrolyte comes in.
After each electron enters the cathode, it reacts with the manganese
dioxide to form MnOO-. Then the MnOO- reacts
with water in the electrolyte solution. The water splits, releasing
hydroxide ions (OH-) and hydrogen ions (H+) that combine
with MnOO- to form MnOOH. The hydroxide ions flow to the anode in the
form of an ionic current.
There, they combine with unstable zinc ions which had given up their
electrons to power the lightbulb. The reaction produces zinc oxide (ZnO)
and water (H2O). The circuit is complete and everybody's
happy.
|
 Call:
Call: Call:
Call:
